explain what it means to characterize a component to be used in a system

Characterization, when used in materials scientific discipline, refers to the wide and general process by which a material'due south structure and backdrop are probed and measured. It is a fundamental process in the field of materials science, without which no scientific understanding of engineering materials could exist ascertained.[1] [ii] The scope of the term oftentimes differs; some definitions limit the term'south utilise to techniques which written report the microscopic structure and properties of materials,[2] while others use the term to refer to whatever materials analysis process including macroscopic techniques such equally mechanical testing, thermal analysis and density adding.[three] The calibration of the structures observed in materials characterization ranges from angstroms, such as in the imaging of individual atoms and chemical bonds, up to centimeters, such as in the imaging of coarse grain structures in metals.
While many characterization techniques have been proficient for centuries, such equally basic optical microscopy, new techniques and methodologies are constantly emerging. In particular the advent of the electron microscope and Secondary ion mass spectrometry in the 20th century has revolutionized the field, allowing the imaging and analysis of structures and compositions on much smaller scales than was previously possible, leading to a huge increase in the level of understanding equally to why different materials evidence different backdrop and behaviors.[4] More recently, diminutive force microscopy has further increased the maximum possible resolution for assay of certain samples in the last 30 years.[v]
Microscopy [edit]

Optical microscopy image of aluminium

Image of a graphite surface at an atomic level obtained past an STM
Microscopy is a category of label techniques which probe and map the surface and sub-surface structure of a textile. These techniques can use photons, electrons, ions or physical cantilever probes to get together information near a sample'due south structure on a range of length scales. Some mutual examples of microscopy techniques include:
- Optical microscopy
- Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
- Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
- Field ion microscopy (FIM)
- Scanning probe microscopy (SPM)
- Diminutive forcefulness microscopy (AFM)
- Scanning tunneling microscopy (STM)
- X-ray diffraction topography (XRT)
Spectroscopy [edit]
Spectroscopy is a category of label techniques which apply a range of principles to reveal the chemical composition, limerick variation, crystal structure and photoelectric properties of materials. Some common examples of spectroscopy techniques include:
Optical radiation [edit]
- Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis)
- Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)
- Thermoluminescence (TL)
- Photoluminescence (PL)
Ten-ray [edit]
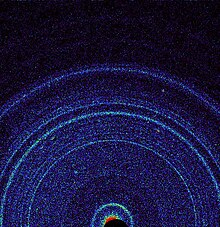
First 10-ray diffraction view of Martian soil - CheMin analysis reveals feldspar, pyroxenes, olivine and more (Marvel rover at "Rocknest", October 17, 2012).[6]

- X-ray diffraction (XRD)
- Pocket-size-bending X-ray scattering (SAXS)
- Energy-dispersive 10-ray spectroscopy (EDX, EDS)
- Wavelength dispersive Ten-ray spectroscopy (WDX, WDS)
- Electron free energy loss spectroscopy (EELS)
- Ten-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS)
- Auger electron spectroscopy (AES)
- X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy (XPCS)[7]
Mass spectrometry [edit]
- Modes of mass spectrometry:
- Electron ionization (EI)
- Thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TI-MS)
- MALDI-TOF
- Secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS)
Nuclear spectroscopy [edit]
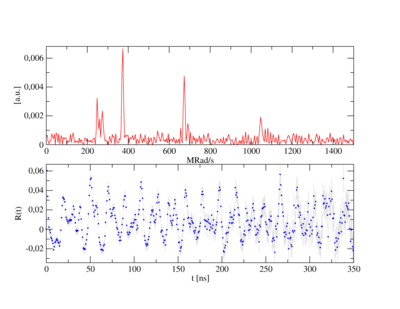
PAC probing the local construction past using radioactive nuclei. From the pattern, electric field gradients are obtained that resolve the construction around the radioactive atom, in social club to study stage transitions, defects, diffusion.
- Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR)
- Mössbauer spectroscopy (MBS)
- Perturbed angular correlation (PAC)
Other [edit]
- Photon correlation spectroscopy/Dynamic light scattering (DLS)
- Terahertz spectroscopy (THz)
- Electron paramagnetic/spin resonance (EPR, ESR)
- Small-angle neutron scattering (SANS)
- Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS)
Macroscopic testing [edit]
A huge range of techniques are used to narrate various macroscopic backdrop of materials, including:
- Mechanical testing, including tensile, compressive, torsional, creep, fatigue, toughness and hardness testing
- Differential thermal assay (DTA)
- Dielectric thermal analysis (DEA, DETA)
- Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)
- Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC)
- Impulse excitation technique (IET)
- Ultrasound techniques, including resonant ultrasound spectroscopy and time domain ultrasonic testing methods[8]

(a) effective refractive indexes and (b) absorption coefficients of integrated circuits obtained via terahertz spectroscopy[9]
See besides [edit]
- Belittling chemistry
- Instrumental chemical science
- Semiconductor characterization techniques
- Wafer bail characterization
- Polymer characterization
- Lipid bilayer characterization
- Lignin label
- Characterization of nanoparticles
- MEMS for in situ mechanical characterization
References [edit]
- ^ Kumar, Sam Zhang, Lin Li, Ashok (2009). Materials characterization techniques. Boca Raton: CRC Press. ISBN978-1420042948.
- ^ a b Leng, Yang (2009). Materials Characterization: Introduction to Microscopic and Spectroscopic Methods. Wiley. ISBN978-0-470-82299-9.
- ^ Zhang, Sam (2008). Materials Characterization Techniques. CRC Printing. ISBN978-1420042948.
- ^ Mathys, Daniel, Zentrum für Mikroskopie, University of Basel: Die Entwicklung der Elektronenmikroskopie vom Bild über die Analyse zum Nanolabor, p. eight
- ^ Patent US4724318 - Diminutive forcefulness microscope and method for imaging surfaces with atomic resolution - Google Patents
- ^ Brown, Dwayne (October 30, 2012). "NASA Rover's Starting time Soil Studies Aid Fingerprint Martian Minerals". NASA. Retrieved October 31, 2012.
- ^ "What is Ten-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS)?". sector7.xray.aps.anl.gov. Archived from the original on 2018-08-22. Retrieved 2016-x-29 .
- ^ R. Truell, C. Elbaum and C.B. Chick., Ultrasonic methods in solid state physics New York, Bookish Press Inc., 1969.
- ^ Ahi, Kiarash; Shahbazmohamadi, Sina; Asadizanjani, Navid (2018). "Quality command and authentication of packaged integrated circuits using enhanced-spatial-resolution terahertz time-domain spectroscopy and imaging". Optics and Lasers in Engineering. 104: 274–284. Bibcode:2018OptLE.104..274A. doi:10.1016/j.optlaseng.2017.07.007.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Characterization_(materials_science)
0 Response to "explain what it means to characterize a component to be used in a system"
Post a Comment